Get your own domain name

A domain name is an URL like http://www.what-ever-you-like.com. There are many benefits on getting your own domain: you get an URL that is easy to remember for your customers, you get an URL that has higher SEO-value (gives higher place in search results), you brand your product directly in the URL and you can get all e-mail addresses that ends with @what-ever-you-like.com. And since a domain name is not very high in price, you get all these benefits very cheap.
If you want to make a website with your own domain address, you will both need to buy a domain address and web hosting.
How is a domain organized?
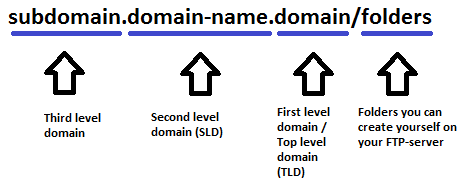
Only the part of the URL address, to the left of the “/”-sign is called the domain. The part to the right is folders you can create on your FTP-server, if you have a web hosting of your website. In this way you can create multiple of folders in many levels.
A domain address is organized in different levels, where level 1 is the part of the domain address to the right, level 2 is the next and so on. All domain addresses have at least two levels, but can have very many levels.
The part of the domain you can choose yourself, is marked in the figure below as domain-name. Mostly the domain-name is second level of the domain, but it might also be the third level, as in domain addresses like something.co.uk, where “uk” is first level, “co” is second level and “something” is third level, but “something” is the domain-name and you can call “co.uk” the “domain” (although the domain is the whole part to the left of the “/”).
When you buy a domain address, you can create multiple addresses, where you put a subdomain to the left of the address.
The First level of the domain is also called Top-level domains (TLDs). This level includes generic TLDs (gTLDs) and country code TLDs (ccTLDs).
Domain names is case insensitive, which means that there is no differens between writing it with capital letters or writing it with small letters. Mostly they are written in small letters.
Domain name System (DNS)
When you enter a domain address in a browser, the DNS (Dynamic Name System) converts the address to an IP address, which is a unique address for all units the internet is composed of (e.g. computers or servers). So instead of entering the IP address directly in the browser, you can enter a domain address, that is easier to remember, into the browser and then get to the unit. You can see the DNS as a kind of phone book on the internet.
The characters aloud in domain names are ASCII characters, but it is also possible to buy domain names containing other Unicode characters, such as Æ, Ø and Å that are used in Denmark. In this case the Unicode character domain is transferred to a ASCII character domain, using a Punycode encoding system, e.g. when you enter høgfeldt.com in your browser it leads you to xn--hgfeldt-q1a.com.
Administration of domains
The rules of the TLDs is managed by ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers). They also have the rights to authorize domain name registrars, companies that have the right to register and reassign domain names.
Each TLD is also maintained by an organisation that holds a registry of all domains that are registered on that TLD.
Both the registrars and the registries can take an annual fee from the domain holder for delegating the domain name. When you buy a domain, you actually buy the right to use the domain name for a year and the right to renew the registration for the next year. The registrar also have a name server, where the link between the domain and IP address is saved.
Sometime a Registry can also be a Registrar. When a registration of a domain has been made, it is written in a database called WHOIS – so this is the database you can find the holder of a domain.
TLDs can either be restricted or not-restricted. When it is restricted, you have to meet to register the domain. It can be that you belong to a certain organization, that you come from a certain country or that your site should have a certain content.
Generic, non-restricted domains
.COM is the most used domain in the world, and is an abbreviation of “commercial”. There are no restrictions in registration of a .COM domain. If you don’t know which domain you want – go for a .COM domain.
.NET is an abbreviation of “network” and is the best alternative to .COM. There are no restrictions, so you can freely use this domain.
.ORG is an abbreviation of “organizations” and was originally used for non-profit organizations, but is today also a domain for schools, communities and other organizations. There are no restrictions in registration of a .ORG domain.
.EDU is a domain that is the abbreviation of “education” and is therefore intended for educational institutions.
.BIZ is a newer domain and is the first phonetic spelling of the first syllable of the word “business”. The domain is intended for use by business sites or commercial sites.
.INFO is also a newer domain and stands for “information”. It is intended for informative sites, however there are no restrictions.
Generic, restricted domains
.GOV stands for “government” and is restricted for use of government sites in USA. So this will not be the domain you will go for.
.MIL is an abbreviation of “military” and is the domain used by the department of defense in USA. It is therefore also a restricted domain.
Country code domains
.CO is actually a domain assigned for Columbia, but everyone can register a .CO domain. It is a very popular domain, because it used to be restricted but isn’t anymore.
.EU is an abbreviation of “European Union” and is non-restricted.
.US is an abbreviation of “United States” and is restricted to citizens and organizations from USA.
.DK is ccTLD for Denmark, .SE for Sweden, .NO for Norway, .DE for germany, .UK for United Kingdom.
Get your own domain
You can buy your own domain name, using one of the registrars that exist. Typically registrars also offers a webhosting solution that your domain name can point at, but they also sell the domain name alone, if you have your own server to point it at. Some recommended registrars of domain names is:
[adrotate banner=”3″] – this is a popular registrar with a really good service